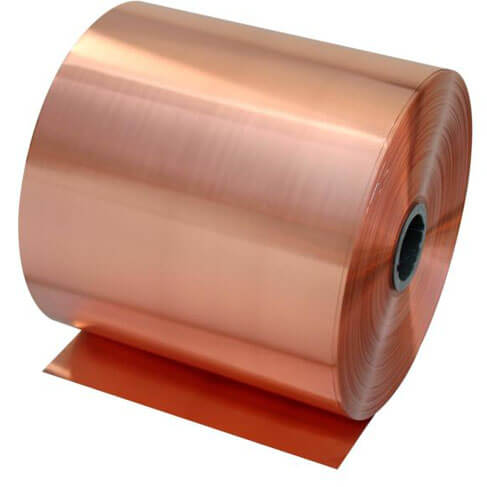
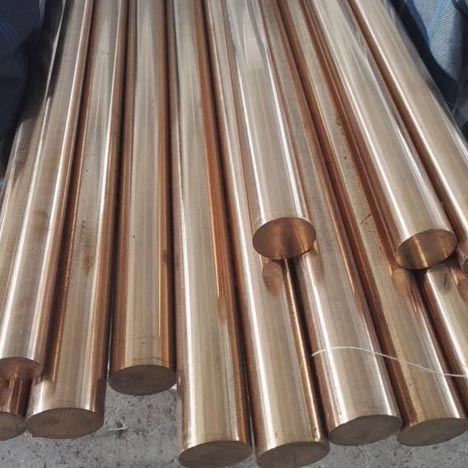
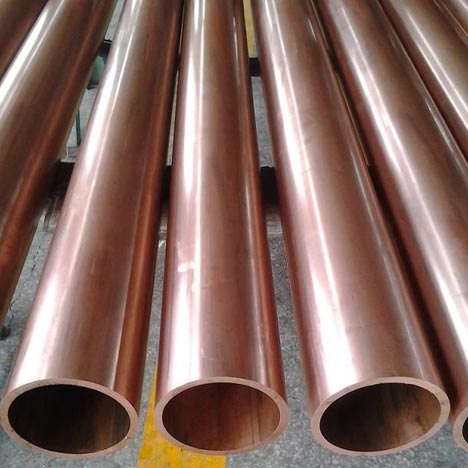
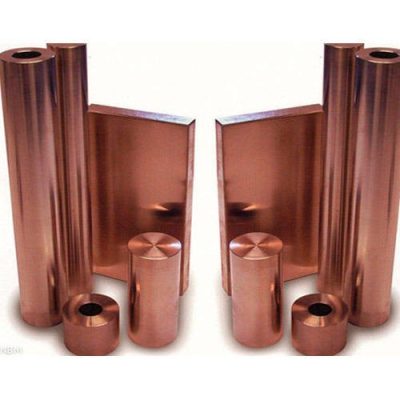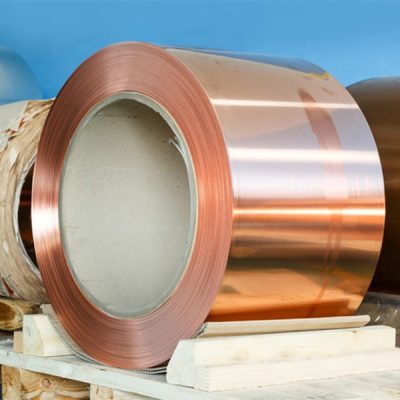




紫銅系列
紫銅是工業純銅。 因其呈玫瑰紅色,氧化膜表面呈紫色,故一般稱為紫銅,又稱紫銅。 它是含有一定量氧的銅,故又稱含氧銅,有時也可視為銅合金。
銅因其紫紅色而得名。 不一定是純銅,有時會添加少量脫氧或其他元素以改善材質和性能。
電子郵件: [email protected]
電話: 0086-13788924073

| Grade list of copper and copper alloys by country | |||||||
| Classification | China | Germany | America | Japan | England | Europe | International |
| oxygen free copper | TU1 | 2.0076 | C10200 | C1020R | C103 | ||
| TU2 | Cu-OF-H110 | C11000 | c1011 | C101 | |||
| Vacuum oxygen free copper | E-Cu58 | TU00 | c1020 | 6N | |||
| high purity | copper-OFE | c10500 | c10700 | ||||
| Silver copper | TAg 0.1 | CuAg 0.1 | C10400 | C1040 | CuAg 0.1 | ||
| brass | H90 | CuZn10 | C22000 | C2200 | CZ101 | CuZn10 | CW501L |
| H70 | CuZn30 | C26000 | C2600 | CZ106 | CuZn30 | CW505L | |
| H68 | C26200 | C2620 | CuZn33 | CW506L | |||
| H65 | CuZn35 | C27000 | C2700 | CZ107 | CuZn36 | CW507L | |
| H63 | CuZn37 | C27200 | C2720 | CZ108 | CuZn37 | CW508L | |
| H62 | CuZn40 | C28000 | C2800 | CZ109 | CW509L | ||
| bronze | QSn4-0.3 | CuSn4 | C51100 | C5111 | PB101 | CuSn4 | CW450K |
| CuSn5 | C51000 | C5101 | CuSn5 | CW451K | |||
| QSn6.5-0.1 | CuSn6 | C51900 | C5191 | PB103 | CuSn6 | CW452K | |
| QSn8-0.3 | CuSn8 | C52100 | C5210 | CuSn8 | CW453K | ||
| QSn6.5-0.4 | |||||||
| copper-nickel | BZn18-18 | CuNi18Zn20 | C75200 | C7521 | NS106 | CuNi18Zn20 | |
| BZn18-26 | CuNi18Zn27 | C77000 | C7701 | NS107 | CuNi18Zn27 | CW410J | |
| BZn15-20 | C7541 | CW409J | |||||
| BZn18-10 | C7350 | ||||||
| pure copper | TU2 | OF-Cu58 | C10100 | C1011 | C101 | CW008A | copper oxide |
| T2 | SW——copper | C11000 | C1100 | C101 | copper - FRHC | ||
| TP2 | SF-Cu | C12200 | C1220 | C106 | CW024A | copper - DHP | |
| TP1 | SW-copper | C12000 | C1201 | CW023A | copper DLP | ||
表現一般
紫銅是純銅的一種,一般可近似認為純銅,導電性、可塑性較好,但強度、硬度較差。 銅具有優良的導熱性、延展性和耐腐蝕性。 銅中的微量雜質對銅的導電性能和導熱性能有嚴重影響。 其中鈦、磷、鐵、矽顯著降低電導率,鎘、鋅影響不大。 硫、硒、碲在銅中的溶解度很小,它們能與銅形成脆性化合物,對導電率影響不大,但會降低加工的塑性。
銅在大氣、海水及一些非氧化性酸(鹽酸、稀硫酸)、鹼、鹽水溶液及多種有機酸(醋酸、檸檬酸)中,具有良好的耐腐蝕性,用於化學工業。 此外,銅具有良好的焊接性,可冷、熱塑加工成各種半成品和成品。 在1970年代,紫銅的產量超過了所有其他銅合金的總產量。
物理特性
銅中的微量雜質對銅的導電性能和導熱性能有嚴重影響。 其中鈦、磷、鐵、矽顯著降低電導率,鎘、鋅影響不大。 氧、硫、硒、碲在銅中的溶解度很小,能與銅形成脆性化合物,對導電率影響不大,但會降低加工的塑性。
普通紫銅在含有氫氣或一氧化碳的還原氣氛中加熱時,氫氣或一氧化碳容易與晶界上的氧化亞銅(Cu2O)作用,產生高壓水蒸氣或二氧化碳氣體,使銅破裂。 這種現象通常被稱為銅的「氫病」。
氧對銅的可焊性有害。 鉍或鉛與銅生成低熔點的共晶,使銅產生熱脆性。 當脆性鉍沿著晶界以薄膜形式分佈時,銅變得冷脆。
磷能顯著降低銅的導電率,但能改善銅液的流動性,並提高焊接性。 適量的鉛、碲、硫等可改善切削加工性。
退火銅板常溫抗拉強度為22~25公斤力/mm 2 ,伸長率為45~50%,布氏硬度(HB)為35~45。
1. 氧乙炔焊接
銅氧乙炔焊可選用焊絲201(或焊絲202)焊絲和焊劑301。 焊接層數較少,焊接後透過錘擊減少焊接應力。
2. 屏蔽金屬弧焊
銅焊條電弧焊可選用銅107或銅227焊條。 電源為直流反接。 焊前預熱溫度為300~500℃。 焊接時採用短弧和直線。 焊接後,對焊縫進行錘擊,以減少焊接應力。
3. 氬弧焊
銅鎢極氬弧焊所用的焊絲和焊劑與氧乙炔焊所用的焊絲和焊劑相同,電源直接接直流電。 焊接前預熱,但溫度不宜過高。
Red copper is used much more widely than pure iron, and every year 50% of the copper is purified by electrolysis for use in the electrical industry. The copper mentioned here should be very pure indeed, and contain more than 99.95% copper. A very small amount of impurities, especially phosphorus, arsenic, aluminum, etc., will greatly reduce the conductivity of copper. It is mainly used for making electric equipment such as generator, bus, cable, switching device, transformer and heat conduction equipment such as heat exchanger, pipe, flat collector of solar heating device. Oxygen in copper (copper smelting is easy to mix with a small amount of oxygen) has a great impact on conductivity, used for electrical industry copper generally must be oxygen-free copper. In addition, lead, antimony, bismuth and other impurities will make the crystallization of copper can not be combined together, resulting in hot brittleness, will also affect the processing of pure copper. This kind of pure copper with high purity is generally refined by electrolysis: the impure copper (coarse copper) is used as anode, the pure copper is used as cathode, and the copper sulfate solution is used as electrolyte. When the current passes through, the impure copper on the anode gradually melts, and the pure copper gradually precipitates on the cathode. The copper thus refined. Purity up to 99.99%.
Copper is also used in motor short circuit ring, electromagnetic heating sensor production and high power electronic components, wiring bar terminals and so on.
Copper is also used in doors, Windows, handrails and other furniture and decoration.
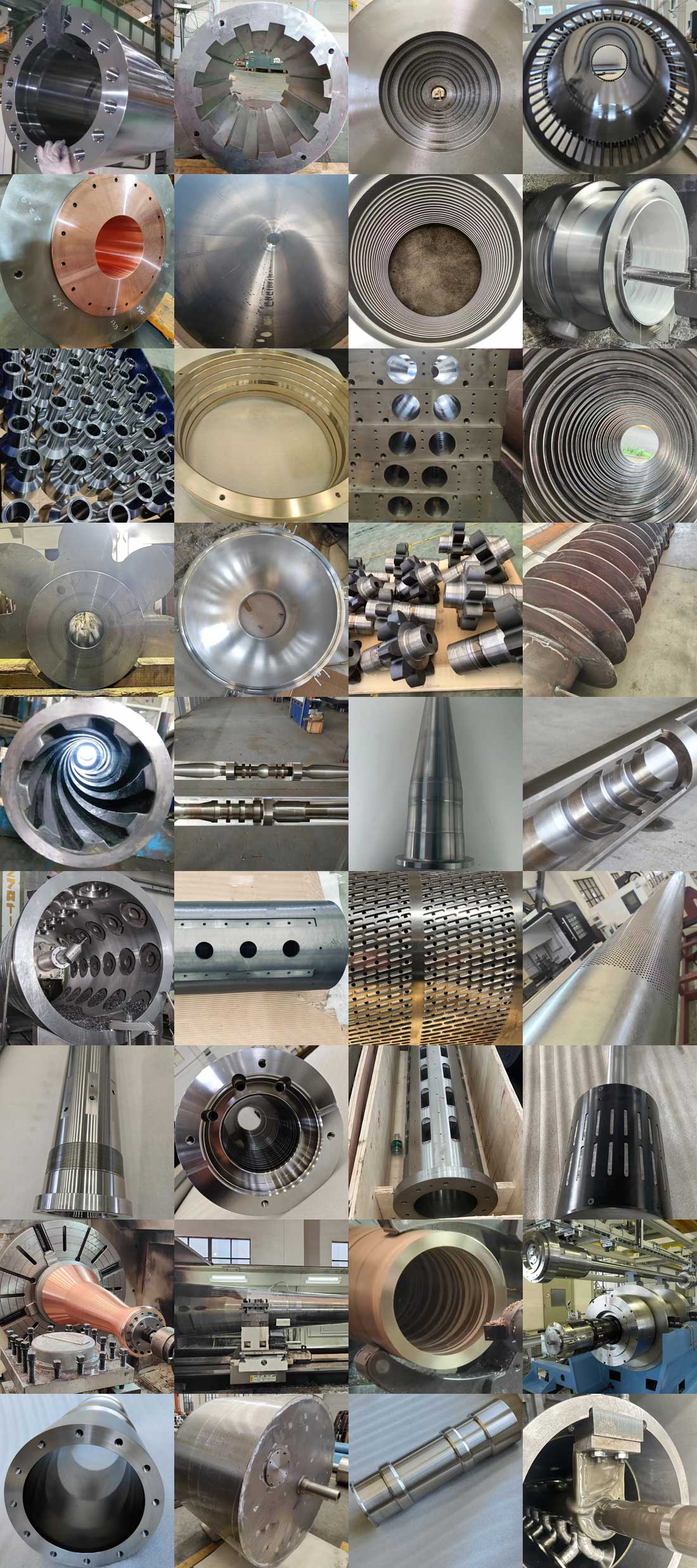
我們還為客戶提供CNC精密加工服務,產品涉及能源,石化,鋼鐵,工程機械,塑膠,防治,液壓,醫療和食品等行業,歡迎發送圖紙詢價。